- The Evolution to Single Party Bids
- Overview of the World Cup Bidding Process:
- Stay Up to Date With New Info
The Evolution to Single Party Bids
This article came about as we received messages inquiring how FIFA awards the hosting rights to interested nation(s). The heightened interest occurred because seemingly out of nowhere, FIFA announced 2030 as decided among the hosts described below and 2034 was all but guaranteed to Saudi Arabia. People inquiring wanted to know when the decisions were made and if FIFA ever changed its policies and processes from the infamous 2015 Corruption Case.
It turns out, this is a loaded question with many complex layers.
A TL;DR style summary
FIFA promised reform after the 2015 Corruption Case and (then FIFA Presidential Candidate and now serving as FIFA President) Gianni Infantino promised transparency and true democracy on host selection.
In the end, a formal Bidding Process was created but one that also opened the gates for some backroom dealings
A More In Depth Look at FIFA’s Evolution From 2015 to Now
We found a solid report from Henry Bushnell at Yahoo Sports that details the evolution, including the near impossible timelines for interested parties to submit a formal bid proposal and the surprise of the FIFA Congress. There’s also comparisons to the IOC’s process for Olympic hosting.
In the end, would there ever be a democratic selection of the World Cup host among 211 delegates without controversy? Likely not.
Does anyone even know the current goal of FIFA in selecting a World Cup host anymore? It’s ok to evolve; however, there needs to be transparency into how and why.
Alas, 2030 and 2034 resulted in single bids which circumvented the entire transparent process that’s detailed below. Perhaps the hosts will still have to adhere to paperwork but would the content even matter?
Again, highly recommend reading Henry Bushnell’s article to compliment the below summary gathered from FIFA’s publicly available documentation.
Overview of the World Cup Bidding Process:
Using 2030 and 2034 as data points since those were recently announced, here’s a summary of the World Cup Bidding Process according to FIFA’s Bid Regulations and FIFA’s Overview of the Bidding Process
The high-level overview of a bidding process contains 5 steps. The 2 steps most people will want to know more details about are the “Bid Evaluation” and “Decision-Making” steps. We’ll detail that in a section below this overview.
High Level Summary
Step 1: High-Level Hosting Requirements
- FIFA establishes key requirements for hosting the World Cup.
- These requirements cover infrastructure, services, commercial, legal support, and sustainability.
- Bidding countries must meet these requirements or risk disqualification.
Note:
For 2034, only FIFA members in AFC (Asia) and OFC (Oceania) Confederations can bid.
Step 2: Written Declaration of Interest
- Eligible countries declare their interest in hosting the World Cup.
- FIFA provides a template agreement detailing their obligations.
Step 3: Bid Preparation
- Bidding countries prepare detailed bids, including infrastructure and plans.
- FIFA may offer support and guidance during this phase.
Step 4: Bid Evaluation
- FIFA evaluates bids using a model that assesses various criteria.
- Criteria include infrastructure, services, commercial potential, and more.
- Bidding countries may need to provide additional information if requested.
Step 5: Decision-Making Process
- Bids that fail to meet minimum requirements are disqualified.
- If necessary, eligible bids are presented to the FIFA Council.
- The FIFA Council designates up to three bids for the FIFA Congress.
- The FIFA Congress then selects the host country(s) in a public vote.
Timeline Example of 2030/2034
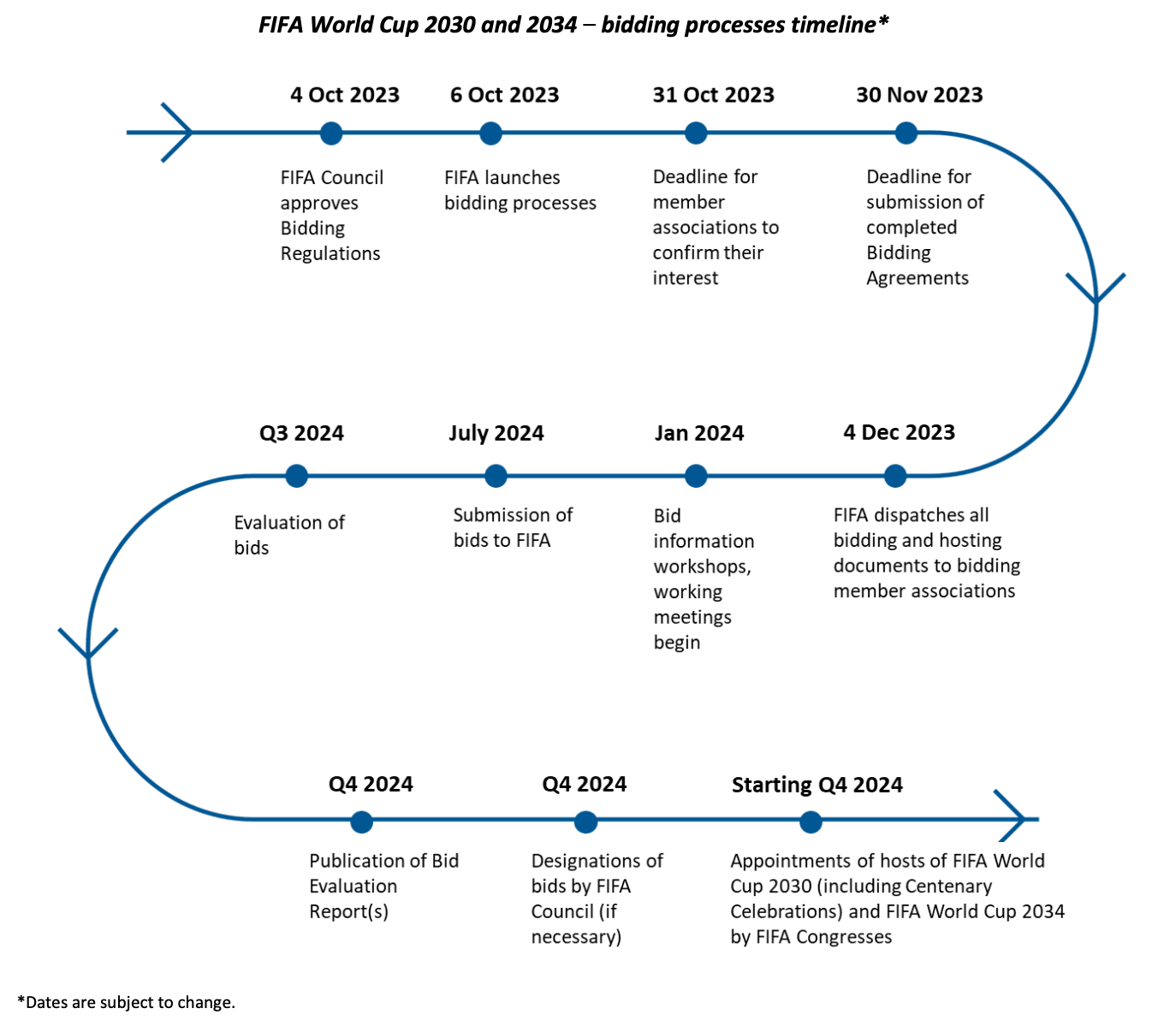
On Page 6 of the Bidding Process Overview from FIFA, this timeline image is used to communicate the estimated dates across the various bidding steps.
Understanding More about World Cup Bid Evaluation Step
Bids are evaluated against specific criteria to receive scores in Risk & Technical Assessment.
Criteria Categories
- Infrastructure
- Stadiums
- Team & Referee Facilities
- Accommodations
- Transport
- International Broadcast Centre (IBC) Sites
- Fan Festival Sites
- Services
- Safety & Security
- Health, Medical & Anti-doping
- IT&T
- Sustainability, Environmental Protection & Human Rights
- Legal & Compliance
- Event Timing
Assessments
- Risk Assessment
- Technical Assessment
World Cup Risk Assessment
All 5 criteria categories are subject to a Risk Assessment Score.
From here, there are 3 Risk Assessment Ratings:
- High Risk
- Medium Risk
- Low Risk
World Cup Technical Assessment
The breakdown of the Technical Assessment Score is:
- 70% – Infrastructure
- 30% – Commercial
Within the 70% Infrastructure criteria, there are weights on each score:
- 35% – Stadiums
- 10% – Team & Referee Facilities
- 7.5% – Accommodations
- 7.5% – Transport
- 5% – IBC Sites
- 5% – Fan Festival Sites
Here’s a breakdown of the scoring system:
- Scores Range: Scores for each criterion range from 0.0 to 5.0.
- Score Categories:
- 0.0 – 1.9: Does not meet minimum requirements
- 2.0 – 2.9: Satisfactory
- 3.0 – 3.9: Good
- 4.0 – 5.0: Very good
HOW are the scores determined for each section?
Great question…no specifics exist at this time, but there’s constant mention of further details being provided so we can only assume and hope this is brought to light later.
What happens if the bids do not meet minimum requirements?
The language is not very concrete. All FIFA states here is that scores “…may have bearing on whether or not the bid is eligible for consideration by, or presentation to, the FIFA Council.“
This leads us to the decision process where each bid has a Bid Evaluation Report.
Understanding More about World Cup Final Decision & Vote
First and foremost, the FIFA Council reviews all submitted bids for initial evaluation and eligibility.
If multiple bids are valid at this point, the FIFA Council designates a maximum of 3 bids for submission to the FIFA Congress.
Once the delegates at the FIFA Congress have the remaining relevant bids, their respective scores, and Bid Evaluation Reports, they assess them holistically. Delegates at the FIFA Congress then make the final selection through a vote, and they publicly announce the results.
Wait, does that mean the delegates of the FIFA Congress can vote however they feel?
It appears that way.
Our interpretation on these documents is that the technical evaluation and risk assessment play crucial roles in in forming one’s opinion of a bid’s eligibility, however the final choice is a democratic one by the members of the FIFA Congress.
Stay Up to Date With New Info
- Use the subscribe option below to receive email updates on new posts and curated info.
- Follow us on X and instagram
- Use options below to rate the information as helpful or unhelpful (& why you thought so)
- If you’d like to discuss a collaboration, send a message





